Saint Mary Magdalene was a woman who, according to the texts included in the New Testament, traveled with Jesus as one of his followers and witnessed Jesus' crucifixion and resurrection. Within the four Gospels she is named at least 12 times, more than most of the apostles and she has been merited the title "Apostle to the apostles" by the Roman Catholic Church. Mary Magdalene is considered to be a saint by the Catholic, Eastern Orthodox, Anglican, and Lutheran churches—with a feast day of July 22. The Eastern Orthodox churches also commemorate her on the Sunday of the Myrrhbearers, the Orthodox equivalent of one of the Western Three Marys traditions. During the Middle Ages, Mary Magdalene was regarded in Western Christianity as a promiscuous woman, claims not found in any of the four canonical gospels. She is a holy patron of Apothecaries; contemplative life; converts; glove makers; hairdressers; penitent sinners; people ridiculed for their piety; perfumeries; pharmacists; sexual temptation; tanners; and women in general.
Shop Online Store
Additional Info
- ID#: 1357-13-294-SP2
- Size: 4 1/3 x 3 1/4 inches (11 x 8 cm)
- Age: ca. 1880
- Origin: Russian Provinces
- Materials: Egg tempera on gessoed wood
- Price: SOLD!
-
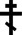
Additional Images of this Item
View the embedded image gallery online at:
https://russianstore.com/en/online-store/russian-icons/item/2941-small-russian-icon-st-mary-magdalene#sigProId52a0b40f36
https://russianstore.com/en/online-store/russian-icons/item/2941-small-russian-icon-st-mary-magdalene#sigProId52a0b40f36
Online Store & Services
Information
Quick Link
Information
Quick Link
SAVE 5% from your first purchase when you subscribe to receive our infrequent mailings with updates on new arrivals, exclusive offers, and fascinating stories on relevant subjects.








 Поменять язык на русский
Поменять язык на русский