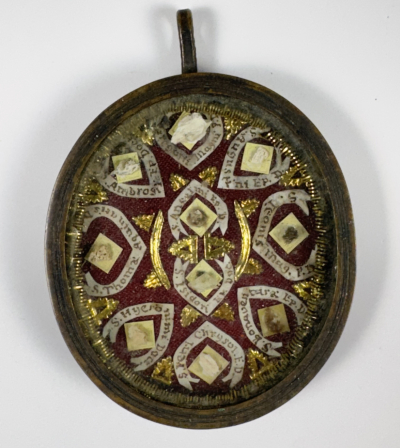
Saint Isidore of Seville (†636) was a Hispano-Roman scholar, theologian, and archbishop of Seville. He is widely regarded as "the last scholar of the ancient world". At a time of disintegration of classical culture, aristocratic violence, and widespread illiteracy, Isidore was involved in the conversion of the Arian Visigothic kings to Chalcedonian Christianity, both assisting his brother Leander of Seville and continuing after his brother's death. His fame after his death was based on his Etymologiae, an etymological encyclopedia that assembled extracts of many books from classical antiquity that would have otherwise been lost. Since the early Middle Ages, Isidore has sometimes been called Isidore the Younger, because of the earlier history purportedly written by Isidore of Córdoba. His Feast Day is commemorated on 4 April.
Saint Anselm of Canterbury (†1109), (also called Anselmo d'Aosta and Anselme du Bec) was an Italian Benedictine monk, abbot, philosopher, and theologian of the Catholic Church, who held the office of Archbishop of Canterbury from 1093 to 1109. As archbishop, he defended the church's interests in England amid the Investiture Controversy. For his resistance to the English kings, he was exiled twice. While in exile, he helped guide the Greek bishops of southern Italy to adopt Roman rites at the Council of Bari. He worked for the primacy of Canterbury over the bishops of York and Wales but, though at his death he appeared to have been successful, Pope Paschal II later reversed himself and restored York's independence. Anselm's canonization was requested of Pope Alexander III by Thomas Becket at the Council of Tours in 1163. He may have been formally canonized before Becket's murder in 1170 but his cult was only formally sanctioned by Pope Alexander VI in 1494. Anselm was proclaimed a Doctor of the Church by Pope Clement XI in 1720; he is known as the doctor magnificus ("Magnificent Doctor") or the doctor Marianus ("Marian doctor"). His Feast Day is 21 April.
Pope Gregory I (†604), commonly known as Saint Gregory the Great, was one of the Latin Fathers and a Doctor of the Church. He is considered a saint in the Catholic Church, Eastern Orthodox Church, Anglican Communion, various Lutheran denominations, and other Protestant denominations. He is known for instituting the first recorded large-scale mission from Rome, the Gregorian mission, to convert the then largely pagan Anglo-Saxons to Christianity. Gregory is also well known for his writings, which were more prolific than those of any of his predecessors as pope. The epithet Saint Gregory the Dialogist has been attached to him in Eastern Christianity because of his Dialogues. Throughout the Middle Ages, he was known as "the Father of Christian Worship" because of his exceptional efforts in revising the Roman worship of his day. His contributions to the development of the Divine Liturgy of the Presanctified Gifts, still in use in the Byzantine Rite, were so significant that he is generally recognized as its de facto author. Immediately after his death, Gregory was canonized by popular acclaim. He is the patron saint of musicians, singers, students, and teachers. His Feast Day is commemorated on 3 September (Latin Church) and 12 March (Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Churches, Anglicanism, Lutheranism).
Saint Augustine of Hippo (†430) was an early Christian theologian and philosopher whose writings influenced the development of Western Christianity and Western philosophy. He was the bishop of Hippo Regius in north Africa and is viewed as one of the most important Church Fathers in Western Christianity for his writings in the Patristic Era. Augustine was canonized by popular acclaim, and later recognized as a Doctor of the Church in 1298 by Pope Boniface VIII. His Feast Day is 28 August, and he is venerated by all Christian denominations which venerate saints. He is considered the patron saint of brewers, printers, theologians, sore eyes, and a number of cities and dioceses.
Saint Pope Leo I (†461) was the first pope to have been called "the Great". He is perhaps best known for having met Attila the Hun in 452 and persuaded him to turn back from his invasion of Italy. He is also a Doctor of the Church, most remembered theologically for issuing the Tome of Leo, a document that was a major foundation for the debates of the Council of Chalcedon, the fourth ecumenical council. That meeting dealt primarily with Christology and elucidated the orthodox definition of Christ's being as the hypostatic union of two natures, divine and human, united in one person, "with neither confusion nor division." It was followed by a major schism associated with Monophysitism, Miaphysitism, and Dyophysitism. He also contributed significantly to developing ideas of papal authority. His Feast Day is commemorated on 10 November and 18 February (Eastern Orthodoxy).
Saint Bonaventure († 1274), was an Italian medieval Franciscan, scholastic theologian and philosopher. The seventh Minister General of the Order of Friars Minor, he was also a Cardinal Bishop of Albano. He was canonized in 1482 by Pope Sixtus IV and declared a Doctor of the Church in 1588 by Pope Sixtus V. He is known as the "Seraphic Doctor". He is ranked along with Thomas Aquinas as the greatest of the Doctors of the Church and was regarded as one of the greatest philosophers of the Middle Ages.
Saint Jerome († 420) was a priest, confessor, theologian and historian, who became a Doctor of the Church. He is best known for his translation of most of the Bible into Latin and he focused his attention to the lives of women and identified how a woman devoted to Jesus should live her life. He is recognised as a saint by the Roman Catholic Church, the Eastern Orthodox Church, the Lutheran Church, and the Church of England. He is a patron of archeologists; archivists; Bible scholars; librarians; libraries; school children; students; and translators.
Saint Thomas Aquinas, OP (†1274) is a Catholic saint and Doctor of the Church who was an Italian Dominican friar and Roman Catholic priest, and an immensely influential philosopher, theologian and jurist in the tradition of scholasticism, within which he is also known as the "Doctor Angelicus" and "Doctor Communis". He is a patron of Academics; against storms; against lightning; apologists; Aquino, Italy; Belcastro, Italy; book sellers; Catholic academies, schools, and universities; chastity; Falena, Italy; learning; pencil makers; philosophers; publishers; scholars; students; University of Sto. Tomas; Sto. Tomas, Batangas; and theologians.
Saint Aurelius Ambrosius (†397), better known in English as Ambrose, was a bishop of Milan who became one of the most influential ecclesiastical figures of the 4th century. Ambrose was a staunch opponent of Arianism and has been accused of fostering persecution of Arians, Jews, and pagans. Traditionally, Ambrose is credited with promoting "antiphonal chant", a style of chanting in which one side of the choir responds alternately to the other, as well as with composing Veni redemptor gentium, an Advent hymn. Ambrose was one of the four original Doctors of the Church and is the patron saint of Milan. His feast day is celebrated on December 7, and he is a patron saint of Beekeepers; bees; bishops; candle makers; domestic animals; the French Commissariat; geese; learning; livestock; Milan; police officers; students; and wax refiners.








 Поменять язык на русский
Поменять язык на русский